Category Archive: Check Valves
What are the Types of Check Valves Used in the Gas Industry?
Check valves are used in pipelines, hoses, and tubing to prevent backflow of liquids and gases. In the gas industry, this helps protect equipment from damage, reduce excessive vibration, and maintain steady production.
A major use for check valves is normalizing the flow of gas during reciprocating compressor discharge in long-distance pipelines. Other natural gas production uses include directing gas flow on metering pumps, hydraulic and air lines, pump discharge, and pressure letdown processes. Check valves are also widely used with gases in oil refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants, and manufacturing facilities.
Here, we’ll look at what check valves are, factors to consider when specifying them, and how they benefit gas industry applications.
What is a Gas Check Valve?
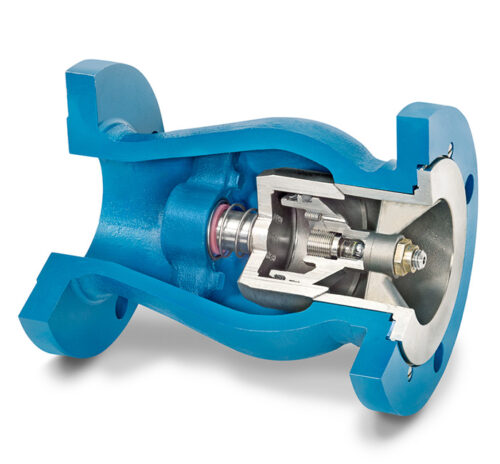 A check valve keeps liquids or gases flowing in a desired direction while preventing them from flowing backward (also called the non-return direction). They are available in many configurations, including threaded, flanged, and space-efficient wafer designs.
A check valve keeps liquids or gases flowing in a desired direction while preventing them from flowing backward (also called the non-return direction). They are available in many configurations, including threaded, flanged, and space-efficient wafer designs.
In an axial flow check valve, gas moves parallel to the axis of rotation through the center of the valve. In-line check valves are placed at predetermined points along a pipeline or tubing system. The valve contains a spring-loaded disc pressed against a gasket to keep the valve closed in its default resting state. When sufficient gas pressure is applied to the disc, it opens and the gas flows through. When pressure drops, the disc closes to prevent the gas from flowing back in the opposite direction. A stem and bushing guide the disc to keep it properly aligned. Nozzle-style check valves are a type of axial flow valve designed specifically for use with low-pressure or intermittent flow liquids or gases.
In natural gas production, check valves are critical for reciprocating compressor discharge. DFT® Inc.’s PDC valve is an ideal solution due to its pulse-dampening chamber, which keeps the disc open during discharge, even as pressure and flow rate may vary. It is a nozzle-style valve with durable carbon or stainless steel construction, a Durlon 9000 gasket, Teflon and Rulon guiding elements, and an Inconel x750 spring for durability and a long service life. As a result, the PDC valve is suitable for a range of uses in the oil, gas, and other industries.
Important Specifications in the Gas Industry
Key factors in specifying gas check valves include:
- Gas Characteristics and Composition. This includes fluid viscosity and specific gravity, corrosiveness, particulate matter, and elemental composition, all of which influence valve size and materials.
- Gas Flow Rate. This influences the size and design of the check valve needed, such as threaded or flanged models. High-flow systems often require larger or multiple valves.
- Temperature. Extreme and/or fluctuating gas and ambient temperatures influence decisions about materials, especially for thermal shock resistance.
- Pressure. Check valves are rated for different operational and maximum pressures in the overall system and in the specific location of the valve.
- Cracking Pressure. This is the minimum pressure needed to open the valve and permit gas flow. If cracking pressure is too high, the valve is harder to open and may slow the flow rate, causing chatter. If it is too low, the time to close the valve increases, since back pressure must overcome forward pressure to close it.
- Operating Environment. This includes horizontal or vertical orientation; accessibility for maintenance in remote locations; gas flow path; vibration, shock, or pulsation in the system; temperatures; and corrosiveness of the environment (e.g., offshore or salt spray exposure).
- Valve Materials. Materials impact the valve’s resistance to environmental conditions and durability over the lifetime of production. They may also affect its ability to stay open or closed for a prolonged time.
- Regulatory Compliance. Check valves used in the oil and gas industry must comply with standards set by the American Petroleum Institute (API), the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Benefits of Check Valves
Check valve technology benefits natural gas production and other processes that use gases in daily operations in these ways:
- Protecting Equipment. Check valves protect pumps and compressor equipment from damage caused by backflow or reverse flow, ensuring systems operate smoothly and without interruption.
- Minimizing Chatter from Turbulence or Pressure Drop. Properly sized and located check valves minimize chatter from the disc opening and closing repeatedly, which contributes to wear on the valve. Chatter is caused by turbulence or drops in flow pressure, and valves that are oversized or too close to the discharge port may not receive adequate pressure to remain open consistently.
- Preventing Slam and Water Hammer. Using the right size valve protects against slamming and hammering from sudden pressure drops, which can damage equipment and pipes or tubing.
- Low Maintenance. Axial flow valves have no external components which protects them from damage and associated repair or replacement.
- Spring-Assisted Design. The spring-assisted design holds the valve disc closed reliably.
- Versatile Installation. Check valves can be oriented vertically or horizontally.
- Tight Shutoff. The spring and gasket ensure a tight seal to prevent leaks.
- Reducing Downtime. Correctly sized check valves help reduce downtime and expenses associated with equipment maintenance or replacement.
- Custom Sizing. Custom sizing is available for certain applications, pressures, and flow rates.
Gas Check Valves from DFT® Inc.
Check valves play a crucial role in the efficiency, safety, and reliability of gas production, oil refining, and similar operations. DFT® check valves offer superior performance, lower maintenance costs, and reassurance against equipment damage due to backflow.
To learn more, visit our DFT® Gas Transmission page to see our PDC and other gas and oil check valve solutions.
Check Valves for Oil & Gas Wells and Produced Water
 With close to 1 million producing oil and natural gas wells in the United States, the industry generates approximately 60 million barrels of produced water daily. This water originates from subsurface reservoirs during the extraction process, where it mixes with oil and gas and emerges at the surface. It can also include water injected into drill rigs or flowback water from hydraulic fracturing operations. Proper handling and disposal are essential to maintain operational efficiency and environmental compliance.
With close to 1 million producing oil and natural gas wells in the United States, the industry generates approximately 60 million barrels of produced water daily. This water originates from subsurface reservoirs during the extraction process, where it mixes with oil and gas and emerges at the surface. It can also include water injected into drill rigs or flowback water from hydraulic fracturing operations. Proper handling and disposal are essential to maintain operational efficiency and environmental compliance.
Saltwater disposal (SWD) is an essential process in the oil and gas industry, managing produced water, a byproduct of extraction operations. Often referred to as saltwater, this water is considered a waste product that is characterized by high salinity and may contain hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and other contaminants. The SWD process often includes pre-treatment steps, such as removing solids and separating residual hydrocarbons, to protect the integrity of the disposal wells. It is then injected into deep underground formations through regulated Class II disposal wells, ensuring it cannot contaminate other subsurface layers and drinking water supplies.
To learn more about the role of check valves in saltwater disposal process download our paper here.
Natural Gas Storage
Natural gas storage and transmission systems are critical components of the energy sector. They allow companies in the industry to effectively balance natural gas production with its consumption. However, such systems are constantly exposed to the erosive flow of solid particles within natural gas that can damage the ductile metal of pipelines or valves, compromising their functionality over time.
Storage systems must also carefully control flow and pressure, requiring components like high-quality natural gas flow check valves and natural gas pressure check valves to help combat these challenges. Learn more about natural gas storage and how check valves maintain the reliability and integrity of natural gas infrastructure.
Basics of Underground Natural Gas Storage
The energy industry typically stores natural gas under pressure in various underground facilities due to the widespread availability of applicable sites. In the U.S., for example, most storage of this odor- and color-free gaseous hydrocarbon is located in emptied natural gas or oil field reservoirs near consumption centers. Salt cavern formations and aquifers are two other common below-ground storage options. To facilitate converting a depleted field from active production to a storage site for natural gas, this approach capitalizes on existing pipeline connections, wells, and gathering systems. Companies in the natural gas sector can also inventory the material above ground, storing it in its gaseous or liquid state within tanks.
However an organization chooses to stockpile its natural gas, its systems and components must be robust enough to handle the mechanical and chemical stresses of high-pressure gas storage and the erosive flow of natural gas transmission. Utilizing high-quality, erosion-resistant valve solutions to manage fluid flow and pressures in your pipelines helps ensure reliable, safe operations with optimized performance.
DFT®’s Check Valves for the Natural Gas Industry
While check valves are available in various sizes, end types, body materials, and pressure classes, the natural gas industry requires high-performance, long-lasting, low-maintenance valves with tight shutoffs to deliver dependable, continuous operation in the field.
At DFT® Inc., we offer an array of check valves that support our clients’ natural gas storage applications. Our PDC® Flanged Check Valve and GLC® Flanged Check Valve are two product options for the natural gas sector. They offer the following features and options:
- Single-piece valve body
- Protected spring with spring-assisted silent close
- Center-guided trim
- Stainless and carbon steel as standard body materials
- Availability in multiple sizes
- Vertical and horizontal installation capabilities
- Compliance with API Specification 6D
PDC®
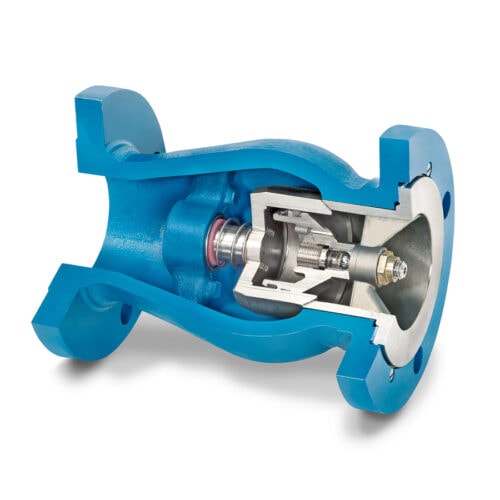

DFT® offers the self-sizing PDC® Flanged Check Valve, designed specifically for natural gas applications. The PDC® valve is rated for ASME pressure classes of 150 to 1500 and is compliant with ASME B16.10 Face-to-Face.
Available in line sizes ranging from 2 to 26 inches, the PDC® is the model we recommend for reciprocating compressor systems in place of piston-type check valves. Our PDC® valve excels in managing the pulsating pressures that these compressors create when they discharge. It achieves this through a specialized pulse-dampening chamber that effectively eradicates valve chatter, a prevalent issue that can lead to premature seat wear and diminished valve performance.
GLC®
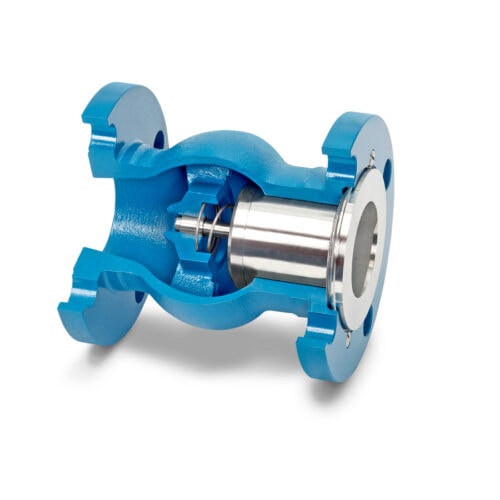

For natural gas lines utilizing other types of compressors, the short-pattern GLC® Flanged Check Valve is ideal. This dual-guided globe-style valve is engineered to minimize pressure loss while offering dependable, low-maintenance performance. Available in sizes 2 to 42 inches, the valve’s design enables a tight seal that’s pivotal in preventing leakage. Ensuring the integrity and efficiency of a natural gas system, the GLC® valve is rated for ASME pressure classes of 150 to 2500.
Advantages of DFT® Check Valves
DFT® has been at the forefront of check and control valve innovation for over 80 years. We utilize stainless and carbon steel in our valves for enhanced erosion and corrosion resistance as well as system longevity. With tens of thousands of valves in service across various sectors, DFT®’s expertise extends to natural gas, compressed gas transmission, and cryogenic liquids.
Our valves are not just components but critical investments in the safety and efficiency of natural gas infrastructure. By mitigating common problems within natural gas storage systems, our PDC® and GLC® Flanged Check Valves are designed to extend your equipment’s lifespan, supporting consistent and reliable operation within the demanding environments of the energy sector.
Natural Gas Check Valves From DFT®
DFT®’s extensive line of check valves is engineered to meet your unique natural gas storage and transmission requirements. Contact our technical team to learn more about our check valves and how we can support your natural gas operations, or request a quote today.
Check Valves in Semiconductor Fabrication
Semiconductors are highly sensitive electronic components that require precision and ultra-clean settings to produce. For creating and maintaining such high-purity conditions in semiconductor fabs, another name for fabrication facilities, manufacturers commonly utilize check valves in their fluid systems. Read on to learn more about the importance of dependable check valves in semiconductor fabrication operations as well as their specific benefits to the industry.
Importance of Check Valves in the Semiconductor Industry
To manufacture semiconductors, fabs require significant amounts of water and steam. Unidirectional check valves are critical components on a pump’s discharge in the fluid systems that deliver or transport these materials. These valves ensure tight seals, offering reliable protection against backflow while enabling smooth and efficient fluid flow. Without check valves, liquids and gases within these systems could flow backward, reverse-spin a pump’s impeller, and damage equipment.
Check valves are also responsible for preventing water hammer, or the surge in pressure that pipes experience as valves suddenly close or pumps shut down. When system fluids come to an abrupt halt, the impact force may cause the fluid to change direction. This is potentially very damaging to valves, pumps, and pipes, as water hammer can create pressure surges up to ten times that of a system’s working pressure.
These valves also keep contaminants from being introduced into the system’s supplies of pure water. While the water in fab processes isn’t the ultra-filtered, ultrapure water, UPW1, that applications like cleanrooms use, the UPW2 that fabs utilize is still exceptionally pure and sufficient for industrial processes.
![]()
Check Valve Applications in Semiconductor Fabrication
Wherever you find a pump in semiconductor fabs, you’ll also find a check valve. They support numerous applications within semiconductor manufacturing, including:
- Generating ultra-pure water
- Controlling water input to cleanroom (WICR) systems
- Processing wastewater
- Operating recirculation pumps
- Running cooling towers
- Cooling
- Rinsing
- Etching
WLC® Wafer Check Valves: The Ideal Choice for Semiconductor Fabs

WLC® Wafer Check Valves are advantageous for their:
- Leak-tight seal for contamination management. Our check valves maintain a tight seal that prevents leaks and removes process liquid and gas contamination risk. This ability is critical to semiconductor manufacturing operations.
- Axial flow design. DFT® engineers check valves for axial flow, which enables them to supply a non turbulent flow of process fluids with minimal pressure drop.
- Damage and downtime prevention. Our WLC® check valves prevent reverse flow, water hammer, and pressure spikes that might otherwise damage equipment, causing costly downtime. As process fluids slow and come to a stop, the spring in the valves’ design quickly seats the internal disc as part of a rapid, reliable closing mechanism.
- Corrosion protection. At DFT®, we only utilize high-quality materials. Our check valves consist of stainless steel, titanium, Hastelloy®, and other such metallurgies to ensure optimal resistance to harsh chemicals and corrosion.
- Silent operation. With their non-slam spring-assisted silent closing, WLC® check valves operate silently, with no slamming or chatter.
- Versatility. Our check valves are compatible with a diverse range of fluids, thermal conditions, and pressures involved in semiconductor fabrication.
- Flexible installation. A distinguishing feature of our check valves is the installation. Unlike a swing check valve, you can install these products vertically (flow up or flow down) or horizontally. This is particularly applicable to cooling tower installations.
- Longevity. These axial flow check valves are designed for long-lasting performance, with minimal maintenance required.
A benefit to partnering with DFT® is our proprietary sizing program. We can custom size our valves to your specific application. Other customization options involve material, pressure, temperature, and flow to support the system’s required cycle rate.
Supporting High-Quality Semiconductor Fabrication With DFT® Valves
Reliable check valves are vital to semiconductor fabrication operations, preventing reverse flow and water hammer while safeguarding equipment and process fluids. At DFT®, our team is backed by more than 80 years of experience helping clients solve their most complex fluid flow challenges. As evidence of our trusted expertise, DFT® has been badged at a major Semiconductor Manufacturer since 1997.
Our ISO 9001-certified company manufactures valves for quality, using methods like leakage rate and hydrostatic testing. Also, our valves are made of materials from certified sources to better create quality products. We balance off-the-shelf offerings with customized valves to ensure you have access to the ideal valve solution for your specific applications. DFT® also carries a significant amount of inventory, allowing us to commonly beat out the competition on lead times.
We take a client-focused, hands-on approach to business to form lasting partnerships with clients in the semiconductor industry and beyond. Contact us for more information on how our check valves support semiconductor fabrication or request a quote today.
PDC® Valves vs. Piston Check Valves
Pulse-dampening check valves, or PDC® valves, are designed for installation on the discharge side of a gas or air reciprocating compressor and feature a pulse-dampening chamber. With this pulse-dampened design, during the momentary pressure and flow increases and reductions that occur with a reciprocating compressor’s cycles, the PDC® valve’s disc remains in the open position, accommodating flow variations and eliminating chatter.
Allowing for either horizontal or vertical installation, these spring-assisted, nozzle-style check valves are used for air or gas and come in line sizes of 2″ to 26″ and ASME Classes 150 to 1500. As for material composition, the one-piece body of this flanged valve is available in either carbon steel or stainless steel, while the center guided trim is composed of stainless steel. You can choose between RF flanged ends or RTJ ends.
These high-performance silent check valves comply with API 6D, a specification set forth by the American Petroleum Institute to govern valve design, production, and testing for natural gas and petroleum applications. They also adhere to the standard ASME B16.10 face-to-face dimensions, as specified by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Compared to piston check valves, PDC® valves offer multiple advantages. Read on to learn more about these valve types and how they differ to determine which is the best option for your needs.
Piston Check Valves
Another variety of check valves is the piston check, which can be used in gas or liquid piping systems. This valve type functions by using a weighted piston, gravity, and backflow pressure. The piston rises up as a result of forward fluid flow within the valve, but when it experiences backflow pressure, spring force pushes the piston seal into the seat to prevent reverse flow.
Some differentiating factors are that with the fluctuations in pressure, such as from a reciprocating compressor, the constant hammering of the piston is not only quite noisy, but over time, the continuous wear the valve incurs can reduce its performance and ultimately lead to premature wear, constant maintenance, or even failure. The internal flow of the piston check is considered a tortuous path, which affects pressure drop. Additionally, the piston check has multiple pressure-retaining components (leak paths), whereas the PDC® is a one-piece body.
DFT®’s PDC® Valves Are Built to Handle Reciprocating Compressor Discharge
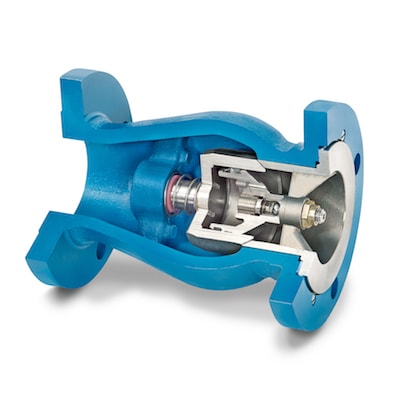 At DFT® Inc., we manufacture our PDC® silent check valves for longer service life and quieter operation. The dampening chamber mitigates a compressor’s pulsed discharge for significant reductions in the wear and tear a piping system will experience. The valve’s unique shape offers the additional benefit of normalizing fluid flow exiting the check valve.
At DFT® Inc., we manufacture our PDC® silent check valves for longer service life and quieter operation. The dampening chamber mitigates a compressor’s pulsed discharge for significant reductions in the wear and tear a piping system will experience. The valve’s unique shape offers the additional benefit of normalizing fluid flow exiting the check valve.
When you’re operating a piping system with an integrated reciprocating compressor, for example, this can cause high-frequency pressure cycling. An installed piston check valve would experience greater wear, impacting additional down-line systems, whereas the PDC® valve offers better protection and more dependable functionality for your application and equipment.
Learn More About Our PDC® Valves
Choosing PDC® check valves from DFT® over piston check valves can enhance the performance, reliability, and longevity of your piping system. This generally equates to a better return on your investment over the lifetime of the valve.
As a world-class manufacturer of control and check valves, DFT® has the multi-industry experience, the resources, and the commitment to excellence and innovation required to produce high-quality valves that address the challenges of each of our customers. We offer an extensive catalog of silent check valve options for solving problems such as water hammer. In addition to our PDC® model, we also have the following available:
- Threaded/socket weld check valves
- Wafer check valves
- Flanged check valves
- Butt weld check valves
- Sanitary check valves
- Restrictor check valves
- Vacuum breaker check valves
- Nickel-aluminum bronze (NAB) check valves
Whatever your application, DFT® is here to help you find the right valve for your unique requirements. Contact our team today to learn more about the PDC® silent check valve difference. You can also explore our PDC® product page or view a 3D animation of the PDC® pulse-dampening effect.