What are the Types of Check Valves Used in the Gas Industry?
Check valves are used in pipelines, hoses, and tubing to prevent backflow of liquids and gases. In the gas industry, this helps protect equipment from damage, reduce excessive vibration, and maintain steady production.
A major use for check valves is normalizing the flow of gas during reciprocating compressor discharge in long-distance pipelines. Other natural gas production uses include directing gas flow on metering pumps, hydraulic and air lines, pump discharge, and pressure letdown processes. Check valves are also widely used with gases in oil refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants, and manufacturing facilities.
Here, we’ll look at what check valves are, factors to consider when specifying them, and how they benefit gas industry applications.
What is a Gas Check Valve?
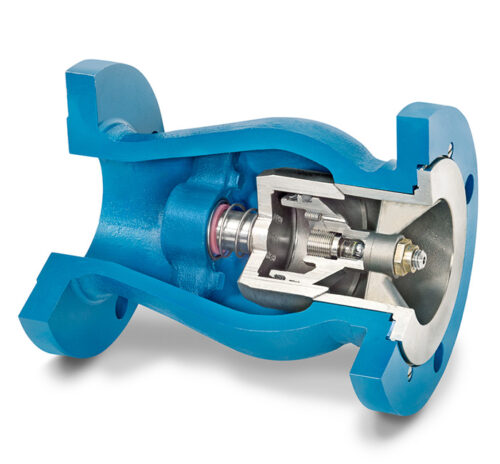 A check valve keeps liquids or gases flowing in a desired direction while preventing them from flowing backward (also called the non-return direction). They are available in many configurations, including threaded, flanged, and space-efficient wafer designs.
A check valve keeps liquids or gases flowing in a desired direction while preventing them from flowing backward (also called the non-return direction). They are available in many configurations, including threaded, flanged, and space-efficient wafer designs.
In an axial flow check valve, gas moves parallel to the axis of rotation through the center of the valve. In-line check valves are placed at predetermined points along a pipeline or tubing system. The valve contains a spring-loaded disc pressed against a gasket to keep the valve closed in its default resting state. When sufficient gas pressure is applied to the disc, it opens and the gas flows through. When pressure drops, the disc closes to prevent the gas from flowing back in the opposite direction. A stem and bushing guide the disc to keep it properly aligned. Nozzle-style check valves are a type of axial flow valve designed specifically for use with low-pressure or intermittent flow liquids or gases.
In natural gas production, check valves are critical for reciprocating compressor discharge. DFT® Inc.’s PDC valve is an ideal solution due to its pulse-dampening chamber, which keeps the disc open during discharge, even as pressure and flow rate may vary. It is a nozzle-style valve with durable carbon or stainless steel construction, a Durlon 9000 gasket, Teflon and Rulon guiding elements, and an Inconel x750 spring for durability and a long service life. As a result, the PDC valve is suitable for a range of uses in the oil, gas, and other industries.
Important Specifications in the Gas Industry
Key factors in specifying gas check valves include:
- Gas Characteristics and Composition. This includes fluid viscosity and specific gravity, corrosiveness, particulate matter, and elemental composition, all of which influence valve size and materials.
- Gas Flow Rate. This influences the size and design of the check valve needed, such as threaded or flanged models. High-flow systems often require larger or multiple valves.
- Temperature. Extreme and/or fluctuating gas and ambient temperatures influence decisions about materials, especially for thermal shock resistance.
- Pressure. Check valves are rated for different operational and maximum pressures in the overall system and in the specific location of the valve.
- Cracking Pressure. This is the minimum pressure needed to open the valve and permit gas flow. If cracking pressure is too high, the valve is harder to open and may slow the flow rate, causing chatter. If it is too low, the time to close the valve increases, since back pressure must overcome forward pressure to close it.
- Operating Environment. This includes horizontal or vertical orientation; accessibility for maintenance in remote locations; gas flow path; vibration, shock, or pulsation in the system; temperatures; and corrosiveness of the environment (e.g., offshore or salt spray exposure).
- Valve Materials. Materials impact the valve’s resistance to environmental conditions and durability over the lifetime of production. They may also affect its ability to stay open or closed for a prolonged time.
- Regulatory Compliance. Check valves used in the oil and gas industry must comply with standards set by the American Petroleum Institute (API), the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Benefits of Check Valves
Check valve technology benefits natural gas production and other processes that use gases in daily operations in these ways:
- Protecting Equipment. Check valves protect pumps and compressor equipment from damage caused by backflow or reverse flow, ensuring systems operate smoothly and without interruption.
- Minimizing Chatter from Turbulence or Pressure Drop. Properly sized and located check valves minimize chatter from the disc opening and closing repeatedly, which contributes to wear on the valve. Chatter is caused by turbulence or drops in flow pressure, and valves that are oversized or too close to the discharge port may not receive adequate pressure to remain open consistently.
- Preventing Slam and Water Hammer. Using the right size valve protects against slamming and hammering from sudden pressure drops, which can damage equipment and pipes or tubing.
- Low Maintenance. Axial flow valves have no external components which protects them from damage and associated repair or replacement.
- Spring-Assisted Design. The spring-assisted design holds the valve disc closed reliably.
- Versatile Installation. Check valves can be oriented vertically or horizontally.
- Tight Shutoff. The spring and gasket ensure a tight seal to prevent leaks.
- Reducing Downtime. Correctly sized check valves help reduce downtime and expenses associated with equipment maintenance or replacement.
- Custom Sizing. Custom sizing is available for certain applications, pressures, and flow rates.
Gas Check Valves from DFT® Inc.
Check valves play a crucial role in the efficiency, safety, and reliability of gas production, oil refining, and similar operations. DFT® check valves offer superior performance, lower maintenance costs, and reassurance against equipment damage due to backflow.
To learn more, visit our DFT® Gas Transmission page to see our PDC and other gas and oil check valve solutions.









Comments are closed